

Lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 11 Feb 2 08:06 access.log -> /dev/stdout In my case, the NGINX UpperDir folder contains the log files: $ ls -la /var/lib/docker/overlay2/585.9eb/diffĭrwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Feb 2 08:06. The read-write layer that represents changes are part of the UpperDir. The LowerDir contains the read-only layers of an image. Let’s explore the content by using an example: $ docker image pull nginx There, you can find different files that represent read-only layers of a Docker image and a layer on top of it that contains your changes.
#DOCKER RUN IMAGE NOT FOUND LOCALLY DRIVER#
If you use the default storage driver overlay2, then your Docker images are stored in /var/lib/docker/overlay2. The heaviest contents are usually images. For example, data for containers, volumes, builds, networks, and clusters. Inside /var/lib/docker, different information is stored. rw-r-r- 1 root root 57 Feb 6 06:56 lowerĭrwx- 2 root root 4.0K Feb 6 06:56 work The internal structure of the Docker root folder ĭrwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4.0K Feb 6 06:56 diff There, you can go to the referenced location: $ cd /var/lib/docker/overlay2/585.9eb/ĭrwx- 4 root root 4.0K Feb 6 06:56. You can connect to the virtual image by: docker run -it -privileged -pid=host debian nsenter -t 1 -m -u -i sh If you inspect regular images then you will get linux paths like: $ docker inspect nginx The configuration and the virtual image to execute linux images are saved in the default Docker root folder. Linux containers are run in a minimal Hyper-V based virtual environment.
#DOCKER RUN IMAGE NOT FOUND LOCALLY WINDOWS#
There are native Windows containers that work similarly to Linux containers. You can kill this session by pressing Ctrl+a, followed by pressing k and y.
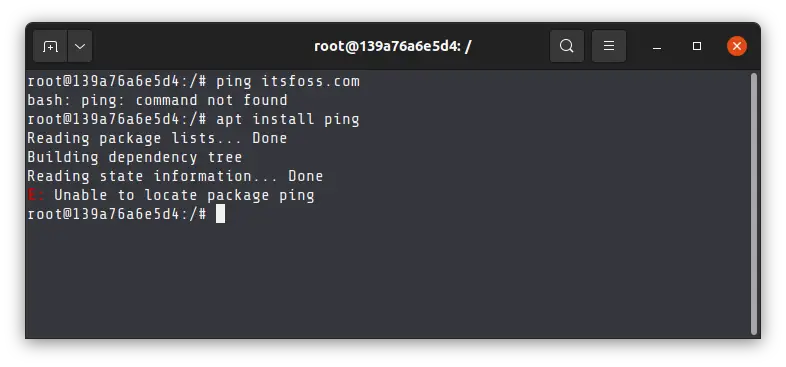
You can investigate your Docker root directory by creating a shell in the virtual environment: $ screen ~/Library/Containers//Data/vms/0/tty Within the virtual image, the path is the default Docker path /var/lib/docker. Docker for Macĭocker is not natively compatible with macOS, so Hyperkit is used to run a virtual image. Therefore, there are some additional things to know. In macOS and Windows, Docker runs Linux containers in a virtual environment.
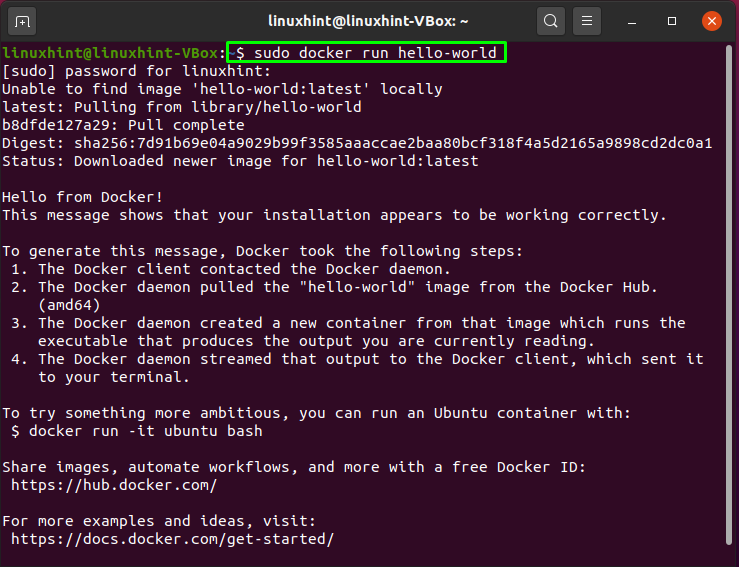
You can get the basic information about your Docker configuration by executing: $ docker info Additionally, it can be used to start applications quickly by executing a single Docker command.Ĭompanies also are investing more and more effort into improving development in local and remote Docker containers, which comes with a lot of advantages as well. Docker has been widely adopted and is used to run and scale applications in production.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
